Cockroaches are among the most common household pests across the world, and they evoke disgust and fear in many people. The question many homeowners ask is: Do cockroaches bite? This article explores this issue in detail, addressing whether cockroaches bite or not, what happens if they do, how one can identify a bite of cockroach, and the best strategies to prevent these pests from becoming a problem in your living space. Through this comprehensive analysis, you will get reliable answers backed by science, expert recommendations, and practical advice. By the end, you will know exactly how to protect yourself and your family.
Cockroach Behavior and Human Interaction
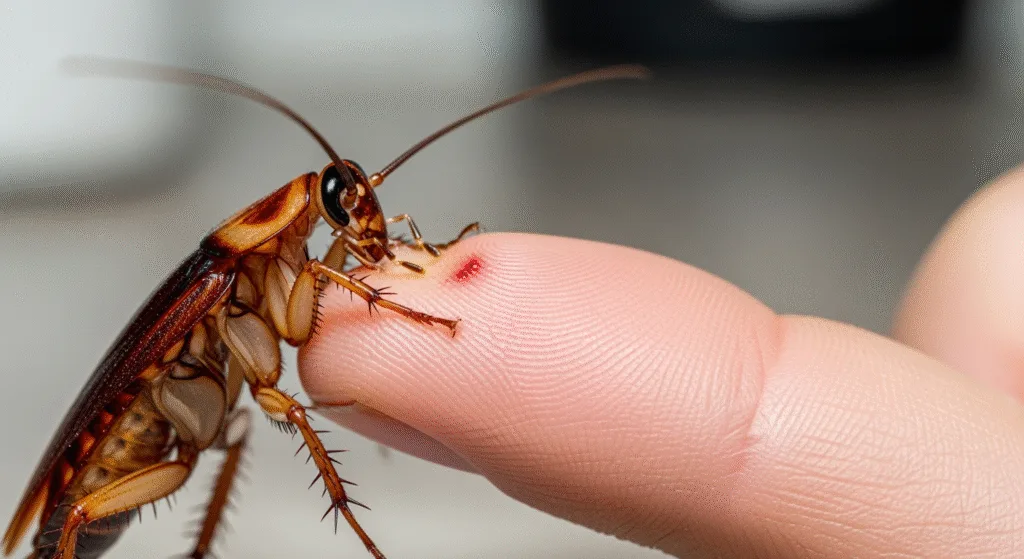

Cockroaches are nocturnal insects that thrive in a wide variety of environments. They seek out food sources in homes, restaurants, garbage areas, and anywhere they can find organic matter. Understanding their behavior is crucial to answering the question of whether they bite humans.
Feeding Habits
Cockroaches are omnivores. They eat scraps of leftover food, decaying matter, cardboard, paper, and even hair or fingernails if food supplies are scarce. Typically, they prefer starchy items, sweets, and fatty substances. They rarely target humans as a food source, but when desperate, they may resort to nibbling on skin, eyelashes, or nails — which can sometimes result in a bite of cockroach.
Activity at Night
Most people encounter cockroaches when they turn on the light in a dark kitchen or bathroom late at night. Cockroaches are more active then, searching for food and water. Because of this nocturnal activity, if biting occurs, it often takes place while a person is asleep.
Why They Approach Humans
Contrary to popular belief, cockroaches do not seek humans out aggressively. They are more attracted to the presence of food particles on a person’s skin, crumbs left around the bed, or even dried saliva on a pillow. These attractants can encourage them to come close, sometimes leading to rare instances of a bite of cockroach.
Do Cockroaches Actually Bite Humans?
The simple answer is yes — cockroaches can bite, but they rarely do. Compared to other pests like bed bugs, mosquitoes, or fleas, cockroaches are not naturally inclined to feed on human blood. Their bites usually occur in environments where infestations are severe, and food sources are limited.
Characteristics of a Bite of Cockroach
- A small red bump that looks similar to a mosquito bite
- Mild swelling, itchiness, or irritation at the site
- Usually occurring on exposed skin like hands, feet, face, or arms
The bite of cockroach is not venomous but can cause discomfort. People who are allergic to cockroaches or have sensitive skin may experience a more noticeable reaction.
Frequency
Cases of humans being bitten by cockroaches are relatively rare. For every household that has roaches, only a few may encounter bites. However, in overpopulated infestations where competition for resources becomes intense, the likelihood increases.
Health Risks Associated with Cockroach Bites
Although cockroach bites are not as dangerous as those from other pests, they still carry certain health risks worth knowing. Cockroaches are carriers of various bacteria, pathogens, and allergens. Thus, a bite of cockroach can occasionally lead to secondary problems.
Possible Infections
When cockroaches bite, they may break the skin. If bacteria from their bodies enter through the wound, infections such as cellulitis may occur. Because cockroaches are known to crawl through trash, sewers, and contaminated places, their bodies often carry Salmonella, E. coli, and other harmful organisms.
Allergic Reactions
Many individuals are allergic to cockroach saliva, feces, or body parts. When a cockroach bite happens, these allergens may intensify symptoms such as itching, rash, or even difficulty breathing for asthmatic patients.
Psychological Effects
Beyond health risks, experiencing a bite of cockroach can also create psychological stress. Knowing that cockroaches are in one’s sleeping area can cause anxiety, sleep deprivation, or increased fear of pest activity at night.
How to Identify a Cockroach Bite
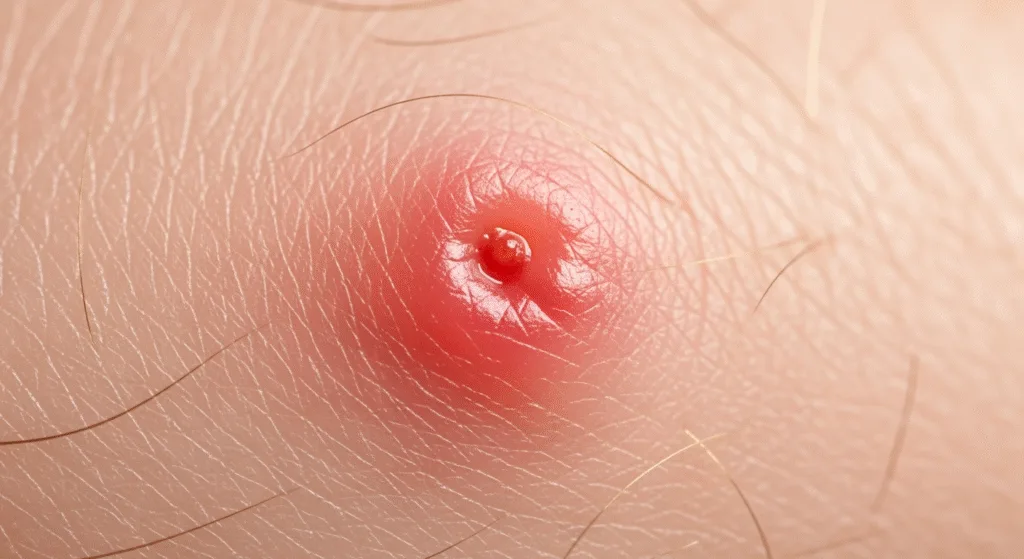
Since cockroach bites resemble mosquito or bed bug marks, identifying them can be tricky. However, there are ways to tell the difference.
Comparison Chart
| Pest Bite | Appearance | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Cockroach | Red, slightly raised bump | Usually occurs on nails, eyelashes, or exposed limbs, often irregular in shape |
| Bed Bug | Clusters or lines of bites | Typically on exposed skin areas, bites often grouped |
| Mosquito | Puffy, round, reddish bump | Often occurs after being outdoors, more itchy |
A bite of cockroach is more random in location, compared to the patterned clusters from bed bugs.
Check for Cockroach Signs
If you suspect the bumps are from cockroaches, look around your home for signs of infestation. Droppings, egg casings, or a musty odor are strong indicators. Finding these alongside skin irritation strengthens the likelihood that you experienced a bite of cockroach.
How to Treat Cockroach Bites
Treating a bite of cockroach is usually simple but necessary to avoid further issues.
Immediate First Aid
- Wash the bite area with soap and warm water
- Apply antiseptic or antibiotic cream to prevent infection
- Use a cold compress to reduce swelling
Home Remedies
Natural remedies can also soothe cockroach bites:
- Aloe vera gel for cooling and reducing irritation
- Baking soda paste to relieve itching
- Honey as a natural antibacterial agent
When to See a Doctor
If the bite of cockroach becomes painful, overly swollen, or shows pus, seek medical attention. Individuals with asthma or severe allergies should consult a physician immediately if they react strongly.
Preventing Cockroaches and Their Bites
The best way to avoid a bite of cockroach is to maintain a cockroach-free environment. Prevention and control combine good hygiene and pest management.
Sanitation Practices
- Wipe food crumbs and spills immediately
- Store food in airtight containers
- Take out trash regularly and keep bins sealed
- Clean under appliances and furniture frequently
Home Maintenance
- Seal cracks and crevices in walls and floors
- Fix leaky pipes and plumbing issues
- Improve ventilation to avoid moist areas
Pest Control Options
If infestations persist, professional help may be needed. Exterminators can apply insecticides or traps that target colonies. DIY methods include using boric acid, gel baits, or diatomaceous earth. However, large populations typically require professional intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cockroach Bites
Are cockroach bites dangerous?
They are not inherently dangerous, but infections or allergic reactions may occur. Careful attention to hygiene helps reduce risks.
Do cockroaches bite during the day?
Cockroaches are nocturnal, so they rarely bite during the day. Most bites occur at night when people sleep.
Can I prevent cockroaches from being near my bed?
Yes. Keep food and crumbs away from sleeping areas, vacuum regularly, and treat infestations promptly.
Where on the body do cockroaches bite most?
Commonly on fingers, hands, nails, feet, and face, especially eyelashes or around the mouth area, since these carry protein traces that attract the insects.
Conclusion
So, do cockroaches bite? The answer is yes — though rarely. A bite of cockroach is not as common as bites from bed bugs or mosquitoes, but it remains possible, especially in heavily infested environments where food is scarce. Knowing how to identify, treat, and prevent these bites ensures your health and peace of mind stay intact. Prevention ultimately comes down to good hygiene, home maintenance, and effective pest control. By keeping your surroundings clean and pest-free, you not only reduce the chances of experiencing cockroach bites but also minimize exposure to the diseases these pests may carry.
Knowledge and preparation are your best defenses. By understanding cockroach behavior and risks, you empower yourself to stay safe and maintain a healthier, more comfortable home environment.



